
The use of MALDI MSI for the study of different tissues
Roman Guran, Lucie Vanickova, Ondrej Zitka, Vojtech Adam and Rene Kizek
The matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) technique was introduced by Karas et al. in 1985 [1]. Three years later, the same research group published a first study on the utilization of this ionization method for mass spectrometry of proteins [2]. Since its introduction, MALDI mass spectrometry was developed rapidly. Nowadays, it is routinely used for characterization of peptides, proteins and identification of bacteria. Because of its soft biomolecules ionization, MALDI was found to be useful for mass spectrometry imaging of a variety of samples where information regarding the spatial distribution of molecules is needed. At the turn of the third millennium, MALDI mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI MSI, MALDI imaging) was firstly applied for the determination of protein expression in mammalian tissues [3]. Usually, MALDI is combined with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF MS), because it measures complete mass spectra over wide mass ranges at the same time [4]. There also exist other types of mass spectrometers connected with MALDI, such as Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers (FT-ICR MS) or linear ion trap with orbitrap mass spectrometers (LTQ Orbitrap MS) [5-7]. Currently, the MALDI MSI technique is the subject of comprehensive research to improve it in different ways – time of analysis [8,9], spatial resolution [10], and sensitivity and detection of different analytes [11,12]. Information gained from MALDI MSI can be correlated with immunohistochemical images [13] or with images from other techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [14] or laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry/atomic emission spectrometry (LA-ICP MS/AES) [15]. There exist several extensive reviews on recent progress in MALDI MSI and on the development of MALDI imaging techniques that are recommended to readers with interest in this field [16-18]. In the following paragraphs, a brief description of the current state of the use of MALDI MSI in research on different analytes in tissues will be given.
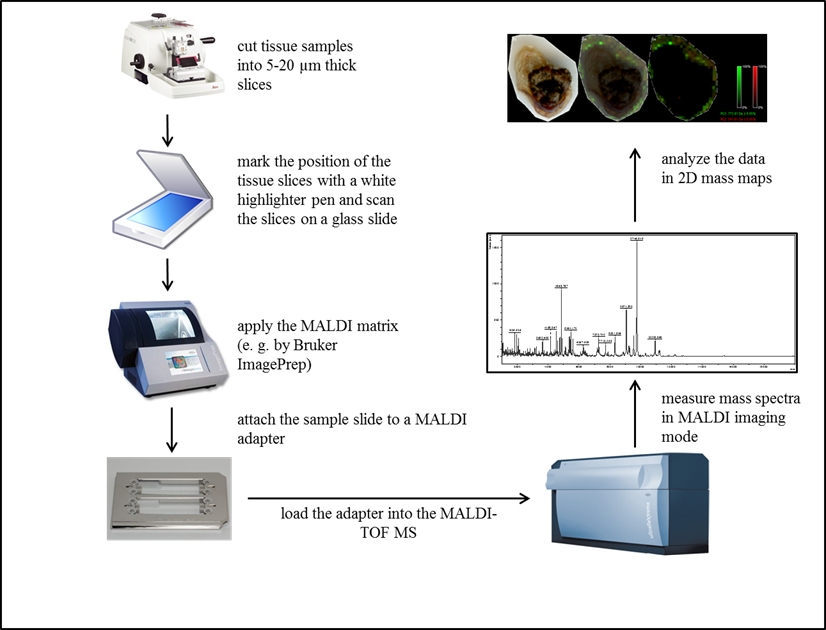
Figure 1: The scheme of typical MALDI MSI workflow.
1. Karas, M.; Bachmann, D.; Hillenkamp, F. Influence of the wavelength in high-irradiance ultraviolet-laser desorption mass-spectrometry of organic-molecules. Analytical Chemistry 1985, 57, 2935-2939.
2. Karas, M.; Hillenkamp, F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10000 Daltons. Analytical Chemistry 1988, 60, 2299-2301.
3. Stoeckli, M.; Chaurand, P.; Hallahan, D.E.; Caprioli, R.M. Imaging mass spectrometry: A new technology for the analysis of protein expression in mammalian tissues. Nature Medicine 2001, 7, 493-496.
4. Caprioli, R.M.; Farmer, T.B.; Gile, J. Molecular imaging of biological samples: Localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Analytical Chemistry 1997, 69, 4751-4760.
5. Solouki, T.; Marto, J.A.; White, F.M.; Guan, S.H.; Marshall, A.G. Attomole biomolecule mass analysis by matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization fourier-transform ion-cyclotron resonance. Analytical Chemistry 1995, 67, 4139-4144.
6. Strupat, K.; Kovtoun, V.; Bui, H.; Viner, R.; Stafford, G.; Horning, S. MALDI produced ions inspected with a linear ion trap-orbitrap hybrid mass analyzer. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2009, 20, 1451-1463.
7. Chen, B.M.; Lietz, C.B.; Li, L.J. In situ characterization of proteins using laserspray ionization on a high-performance MALDI-LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2014, 25, 2177-2180.
8. Bednarik, A.; Kuba, P.; Moskovets, E.; Tomalova, I.; Krasensky, P.; Houska, P.; Preisler, J. Rapid matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry imaging with scanning desorption laser beam. Analytical Chemistry 2014, 86, 982-986.
9. Prentice, B.M.; Chumbley, C.W.; Caprioli, R.M. High-speed MALDI MS/MS imaging mass spectrometry using continuous raster sampling. Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2015, 50, 703-710.
10. Korte, A.R.; Yandeau-Nelson, M.D.; Nikolau, B.J.; Lee, Y.J. Subcellular-level resolution MALDI-MS imaging of maize leaf metabolites by MALDI-linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2015, 407, 2301-2309.
11. Flinders, B.; Morrell, J.; Marshall, P.S.; Ranshaw, L.E.; Clench, M.R. The use of hydrazine-based derivatization reagents for improved sensitivity and detection of carbonyl containing compounds using MALDI-MSI. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2015, 407, 2085-2094.
12. Wang, X.D.; Han, J.; Yang, J.C.; Pan, J.X.; Borchers, C.H. Matrix coating assisted by an electric field (MCAEF) for enhanced tissue imaging by MALDI-MS. Chemical Science 2015, 6, 729-738.
13. Caldwell, R.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Oppenheimer, S.R.; Schwartz, H.S.; Caprioli, R.M. Molecular assessment of the tumor protein microenvironment using imaging mass spectrometry. Cancer Genomics & Proteomics 2006, 3, 279-287.
14. Acquadro, E.; Cabella, C.; Ghiani, S.; Miragoli, L.; Bucci, E.M.; Corpillo, D. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization imaging mass spectrometry detection of a magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent in mouse liver. Analytical Chemistry 2009, 81, 2779-2784.
15. Bianga, J.; Bouslimani, A.; Bec, N.; Quenet, F.; Mounicou, S.; Szpunar, J.; Bouyssiere, B.; Lobinski, R.; Larroque, C. Complementarity of MALDI and LA ICP mass spectrometry for platinum anticancer imaging in human tumor. Metallomics 2014, 6, 1382-1386.
16. Dreisewerd, K. Recent methodological advances in MALDI mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2014, 406, 2261-2278.
17. Rompp, A.; Spengler, B. Mass spectrometry imaging with high resolution in mass and space. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 2013, 139, 759-783.
18. Svatos, A. Mass spectrometric imaging of small molecules. Trends in Biotechnology 2010, 28, 425-434.
19. Sun, N.; Ly, A.; Meding, S.; Witting, M.; Hauck, S.M.; Ueffing, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A. High-resolution metabolite imaging of light and dark treated retina using MALDI- FTICR mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2014, 14, 913-923.
20. Wang, H.Y.J.; Wu, H.W.; Tsai, P.J.; Liu, C.B.; Zheng, Z.F. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging of cardiolipins in rat organ sections. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2014, 406, 565-575.
21. Shroff, R.; Schramm, K.; Jeschke, V.; Nemes, P.; Vertes, A.; Gershenzon, J.; Svatos, A. Quantification of plant surface metabolites by matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization mass spectrometry imaging: Glucosinolates on Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Plant Journal 2015, 81, 961-972.
22. Louie, K.B.; Bowen, B.P.; Cheng, X.L.; Berleman, J.E.; Chakraborty, R.; Deutschbauer, A.; Arkin, A.; Northen, T.R. „Replica-extraction-transfer“ nanostructure-initiator mass spectrometry imaging of acoustically printed bacteria. Analytical Chemistry 2013, 85, 10856-10862.
23. Nimesh, S.; Mohottalage, S.; Vincent, R.; Kumarathasan, P. Current status and future perspectives of mass spectrometry imaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2013, 14, 11277-11301.
24. Kriegsmann, J.; Kriegsmann, M.; Casadonte, R. MALDI TOF imaging mass spectrometry in clinical pathology: A valuable tool for cancer diagnostics. International Journal of Oncology 2015, 46, 893-906.
25. Thomas, A.; Chaurand, P. Advances in tissue section preparation for MALDI imaging MS. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 967-982.
26. Wang, J.N.; Qiu, S.L.; Chen, S.M.; Xiong, C.Q.; Liu, H.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, N.; Hou, J.; He, Q.; Nie, Z.X. MALDI-TOF MS imaging of metabolites with a N (1 naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride matrix and its application to colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Analytical Chemistry 2015, 87, 422-430.
27. Buck, A.; Halbritter, S.; Spath, C.; Feuchtinger, A.; Aichler, M.; Zitzelsberger, H.; Janssen, K.P.; Walch, A. Distribution and quantification of irinotecan and its active metabolite SN-38 in colon cancer murine model systems using MALDI MSI. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2015, 407, 2107-2116.
28. Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Zitka, O.; Krizkova, S.; Moulick, A.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. MALDI-TOF MS as evolving cancer diagnostic tool: A review. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2014, 95, 245-255.
29. Krasny, L.; Hoffmann, F.; Ernst, G.; Trede, D.; Alexandrov, T.; Havlicek, V.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; von Eggeling, F.; Crecelius, A.C. Spatial segmentation of MALDI FT-ICR MSI data: A powerful tool to explore the head and neck tumor in situ lipidome. Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2015, 26, 36-43.
30. Huber, K.; Aichler, M.; Sun, N.; Buck, A.; Li, Z.; Fernandez, I.E.; Hauck, S.M.; Zitzelsberger, H.; Eickelberg, O.; Janssen, K.P., et al. A rapid ex vivo tissue model for optimising drug detection and ionisation in MALDI imaging studies. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 2014, 142, 361-371.
31. Vegvari, A.; Fehniger, T.E.; Rezeli, M.; Laurell, T.; Dome, B.; Jansson, B.; Welinder, C.; Marko-Varga, G. Experimental models to study drug distributions in tissue using MALDI mass spectrometry imaging. Journal of Proteome Research 2013, 12, 5626-5633.
32. Zecchi, R.; Trevisani, M.; Pittelli, M.; Pedretti, P.; Manni, M.E.; Pieraccini, G.; Pioselli, B.; Amadei, F.; Moneti, G.; Catinella, S. Impact of drug administration route on drug delivery and distribution into the lung: An imaging mass spectrometry approach. European Journal of Mass Spectrometry 2013, 19, 475-482.
33. Mondon, P.; Hillion, M.; Peschard, O.; Andre, N.; Marchand, T.; Doridot, E.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Pionneau, C.; Chardonnet, S. Evaluation of dermal extracellular matrix and epidermal-dermal junction modifications using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging, in vivo reflectance confocal microscopy, echography, and histology: Effect of age and peptide applications. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology 2015, 14, 152-160.
34. Cuypers, E.; Flinders, B.; Bosman, I.J.; Lusthof, K.J.; Van Asten, A.C.; Tytgat, J.; Heeren, R.M.A. Hydrogen peroxide reactions on cocaine in hair using imaging mass spectrometry. Forensic Science International 2014, 242, 103-110.
35. Poetzsch, M.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Steuer, A.E.; Kraemer, T. Segmental hair analysis for differentiation of tilidine intake from external contamination using LC-ESI-MS/MS and MALDI-MS/MS imaging. Drug Testing and Analysis 2015, 7, 143-149.
36. Bradshaw, R.; Bleay, S.; Clench, M.R.; Francese, S. Direct detection of blood in fingermarks by MALDI MS profiling and imaging. Science & Justice 2014, 54, 110-117.
37. Ly, A.; Schone, C.; Becker, M.; Rattke, J.; Meding, S.; Aichler, M.; Suckau, D.; Walch, A.; Hauck, S.M.; Ueffing, M. High-resolution MALDI mass spectrometric imaging of lipids in the mammalian retina. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 2015, 143, 453-462.
38. Rocha, B.; Cillero-Pastor, B.; Eijkel, G.; Bruinen, A.L.; Ruiz-Romero, C.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Blanco, F.J. Characterization of lipidic markers of chondrogenic differentiation using mass spectrometry imaging. Proteomics 2015, 15, 702-713.
39. Soares, M.S.; da Silva, D.F.; Forim, M.R.; da Silva, M.F.d.G.F.; Fernandes, J.B.; Vieira, P.C.; Silva, D.B.; Lopes, N.P.; de Carvalho, S.A.; de Souza, A.A., et al. Quantification and localization of hesperidin and rutin in Citrus sinensis grafted on C. limonia after Xylella fastidiosa infection by HPLC-UV and MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 2015, 115, 161-170.
40. Kusari, S.; Sezgin, S.; Nigutova, K.; Cellarova, E.; Spiteller, M. Spatial chemo-profiling of hypericin and related phytochemicals in Hypericum species using MALDI-HRMS imaging. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2015, 407, 4779-4791.
41. Annangudi, S.P.; Myung, K.; Adame, C.A.; Gilbert, J.R. MALDI-MS imaging analysis of fungicide residue distributions on wheat leaf surfaces. Environmental Science & Technology 2015, 49, 5579-5583.
42. Klein, A.T.; Yagnik, G.B.; Hohenstein, J.D.; Ji, Z.Y.; Zi, J.C.; Reichert, M.D.; MacIntosh, G.C.; Yang, B.; Peters, R.J.; Vela, J., et al. Investigation of the chemical interface in the soybean-aphid and rice-bacteria interactions using MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging. Analytical Chemistry 2015, 87, 5294-5301.
43. Bhandari, D.R.; Schott, M.; Rompp, A.; Vilcinskas, A.; Spengler, B. Metabolite localization by atmospheric pressure high-resolution scanning microprobe matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging in whole-body sections and individual organs of the rove beetle Paederus riparius. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 2015, 407, 2189-2201.
44. Nunes, T.M.; Mateus, S.; Favaris, A.P.; Amaral, M.; von Zuben, L.G.; Clososki, G.C.; Bento, J.M.S.; Oldroyd, B.P.; Silva, R.; Zucchi, R., et al. Queen signals in a stingless bee: Suppression of worker ovary activation and spatial distribution of active compounds. Scientific Reports 2014, 4.
45. Niehoff, A.C.; Kettling, H.; Pirkl, A.; Chiang, Y.N.; Dreisewerd, K.; Yew, J.Y. Analysis of Drosophila lipids by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging. Analytical Chemistry 2014, 86, 11086-11092.
J.Met.Nano:
volume-2, issue-3
- Laboratory of Metallomics and Nanotechnologies – an initiator of the Metallomics Scientific Network formation
- Capillary electrophoresis of metallothionein
- Synthetic birnessites and buserites as heavy metal cation traps and environmental remedies
- Immunohistochemical detection of metallothionein
- MALDI-TOF MSI and electrochemical detection of metallothionein in chicken liver after cadmium exposure
- The use of MALDI MSI for the study of different tissues
- Utilization of graphene oxide electrophoretic deposition for construction of electrochemical sensors and biosensors
- Influence of Different Inducers on Ligninolytic Enzyme Activities
- Interaction of nanocarrier apoferritin with cytotoxic drug molecules
- Study of cell penetrating peptide and Europium(III) and Terbium(III) Schiff base complexes interaction
- HPV Detection in Leukocyte Samples of Spinocellular Carcinomas Using PCR
- Characterization of carbon quantum dots by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detections
- Modification of anti-DNA antibodies with carbon quantum dots
- Fluorescence detection of carbon quantum dots assessed by stratospheric platform
 PDF
PDF