

Učit se znamená objevovat to, co už víš.
Konat znamená demonstrovat, že to to víš.
Učit druhé znamená připomínat jim, že to vědí stejně dobře jako ty.
Všichni jste zároveň žáci, praktikanti a učitelé.
Richard Bach
Literatura
Byly zveřejněny nové hodnoty Impact Factor
 Vice podrobností naleznete na adrese
Vice podrobností naleznete na adrese
http://admin-apps.webofknowledge.com/JCR/JCR?RQ=LIST_SUMMARY_JOURNAL
Podívejte se do JACS
 The 20S proteasome core particle is a molecular machine that plays a central role in the regulation of cellular function through proteolysis, and it has emerged as a valuable drug target for certain classes of cancers. Central to the development of new and potent pharmaceuticals is an understanding of the mechanism by which the proteasome cleaves substrates. A number of high-resolution structures of the 20S proteasome with and without inhibitors have emerged that provide insight into the chemistry of peptide bond cleavage and establish the role of Thr1 O?1 as the catalytic nucleophile. The source of the base that accepts the Thr1 H?1 is less clear. Using a highly deuterated sample of the proteasome labeled with 13CH3 at the Thr-? positions, the pKA of the Thr1 amino group has been measured to be 6.3 and hence deprotonated in the range of maximal enzyme activity. This provides strong evidence that the terminal amino group of Thr1 serves as the base in the first step of the peptide bond cleavage reaction.
The 20S proteasome core particle is a molecular machine that plays a central role in the regulation of cellular function through proteolysis, and it has emerged as a valuable drug target for certain classes of cancers. Central to the development of new and potent pharmaceuticals is an understanding of the mechanism by which the proteasome cleaves substrates. A number of high-resolution structures of the 20S proteasome with and without inhibitors have emerged that provide insight into the chemistry of peptide bond cleavage and establish the role of Thr1 O?1 as the catalytic nucleophile. The source of the base that accepts the Thr1 H?1 is less clear. Using a highly deuterated sample of the proteasome labeled with 13CH3 at the Thr-? positions, the pKA of the Thr1 amino group has been measured to be 6.3 and hence deprotonated in the range of maximal enzyme activity. This provides strong evidence that the terminal amino group of Thr1 serves as the base in the first step of the peptide bond cleavage reaction.

Je otevřen přístup do database časopisů ACS z MENDELU přístupového bodu. Využijte tyto přístupy maximální míře. http://pubs.acs.org/
Current Protocols
V rámci řešení projektu MENDELU RESEARCH LIBRARY http://mereli.mendelu.cz/ byl na webových stránkách http://www.mendelu.cz/cz/sluzby_sz/icuk/databaze
zpřístupněn nový elektronický informační zdroj a to Wiley Current Protocols
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/browse/publications?type=labprotocols. Jedná se o trvalý nákup Current Protocols publikovaných 2013-2017.
Novinky z knihovny
dovoluji si Vás upozornit, že některé z knih, které jsme se rozhodli zakoupit z projektu SCI-INFO, jsou již k dispozici. Naleznete je v databázi EBSCO (http://search.ebscohost.com) v oddělení EBSCO eBooks - VUT eBooks pro STM. Knihy jsou vyhledatelné i z normálního rozhraní EBSCO.
Prima ZOOM
Metalothionein information servis (26 T)
Title: The effect of zinc and the role of p53 in copper-induced cellular stress responses
Author(s): Formigari, Alessia; Gregianin, Elisa; Irato, Paola
Source: JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY Volume: 33 Issue: 7 Pages: 527-536 DOI: 10.1002/jat.2854 Published: JUL 2013
Metals can directly or indirectly cause an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in cells, and this may result in programmed cell death. A number of previous studies have shown that zinc (Zn) modulates mitogenic activity via several signalling pathways, such as AKT, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF -B), AP-1 and p53. The exact role that Zn plays in the regulation of apoptosis remains ambiguous. Intracellular free Zn modulates p53 activity and stability, and excess Zn alters the p53 protein structure and down-regulates p53's binding to DNA. Copper (Cu) accumulation causes apoptosis that seems to be mediated by DNA damage and subsequent p53 activation. Cu can also displace Zn from its normal binding site on p53, resulting in abnormal protein folding and disruption of p53 function. In spite of the induction of the tumour suppressor p53, hepatic Cu accumulation significantly increases the risk of cancerous neoplasm both in humans and rats, suggesting that p53 function may be impaired in these cells. It is generally understood that imbalances in Cu and Zn levels may lead to a higher prevalence of p53 mutations. An increased number of p53 mutations have been found in liver samples from Wilson's disease (WD) patients. High levels of the p53 mutation most probably contribute to the pathogenesis of cancer in individuals with WD, but the cause and effect are not clear. The protein p53 also plays a crucial role in the transcriptional regulation of metallothionein, which indicates a novel regulatory role for p53. This review discusses the central role of p53 and the redox-inert metal Zn in the cellular stress responses induced by the redox active biometal Cu. Copyright (c) 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Title: Proteomic characterization of the late and persistent effects of cadmium at low doses on the rat liver
Author(s): Wang, Bo; Wang, Shi; Shao, Chen; et al.
Source: JOURNAL OF APPLIED TOXICOLOGY Volume: 33 Issue: 7 Pages: 546-557 DOI: 10.1002/jat.1757
Abstract: To investigate the late and persistent effects of cadmium (Cd) at low doses on the liver and its potential mechanisms, male Wistar rats were given i.p. injection of Cd as CdCl2 at 20nmolkg1 body weight every other day for 4weeks. At weeks 20, 44 and 52, the livers from Cd-treated and age-matched control rats were examined pathologically and biochemically. Chronic exposure of rats to Cd at low doses induced mild pathological changes and persistent oxidative damage as well as cell proliferation. Hepatic proteins were analyzed with two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) and mass spectrometry. More than 1000 protein spots were detected by 2-DE. Ten proteins were distinguishable between Cd-treated and age-matched control groups at week 52week after Cd treatment. Two of them were significantly down-regulated: prohibitin (PHB) and d-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT). By western blotting the down-regulated expression of PHB and DDT in the livers of Cd-treated rats was confirmed in both early (week 20) and late (week 52) time points. To further examine the down-regulation of antioxidant status in the Cd-treated livers, other common antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase and glutathione and one metal detoxification specific protein metallothionein, were also detected and found to be decreased, particularly at the late stage. These results suggest that mild histopathological changes, persistent oxidative damage and cell proliferation remained at the late stages (weeks 4452) after rats were exposed to low-dose Cd. These persistent changes may be associated with the persistent down-regulation of cellular antioxidant systems. Copyright (c) 2011 John Wiley & Sons, LtdPublished: JUL 2013
Title: Genetic structure and heterozygosity-fitness correlation in young-of-the-year sole (Solea solea L.) inhabiting three contaminated West-European estuaries
Author(s): Guinand, B.; Fustier, M. A.; Labonne, M.; et al.
Source: JOURNAL OF SEA RESEARCH Volume: 80 Pages: 35-49 DOI: 10.1016/j.seares.2013.02.006 Published: JUL 2013
Title: Different mechanisms for metal-induced adaptation to cadmium in the human lung cell lines A549 and H441
Author(s): Sauvageau, Josee-Anne; Jumarie, Catherine
Source: CELL BIOLOGY AND TOXICOLOGY Volume: 29 Issue: 3 Pages: 159-173 DOI: 10.1007/s10565-013-9243-4 Published: JUN 2013
Abstract: Sensitivity to Cd and Zn as well as the capacity to develop tolerance were characterized in human lung cells A549 and H441. In the A549 cells, a 2-fold lower LC50 was obtained for Cd compared to Zn, whereas H441 cells were similarly sensitive to both metals. H441 cells were twice as resistant to Cd as the A549 cells. Higher HSP70, but not metallothionein (MT) or glutathione (GSH) levels, could contribute to this better resistance. A 1.5- and 2-fold increase in the LC50 for Cd was obtained in the A549 cells pre-exposed to non-cytotoxic concentrations of Cd (20 mu M) or Zn (40 mu M) for 24 h. On the other hand, only Zn increased H441 cells' resistance to Cd. Maximum Zn- and Cd-induced tolerances were reached as early as 3 and 12 h, respectively. Increases in MT-IIa and HSP70 messenger RNA levels were higher in A549 cells, but cycloheximide eliminated the induction of tolerance only in the H441 cells. Protein synthesis is a prerequisite for metal-induced tolerance to Cd in the H441 cells but not the A549 cells. Results obtained with l-buthionine sulfoximine revealed that GSH synthesis is not responsible for the acquired tolerance in both cell lines. However, GSH plays a critical role against Cd toxicity, and pro-oxidant conditions sensitized cells to Cd with different impacts on the metal-induced mechanisms of acquired tolerance. GSH and catalase both provide antioxidative protection, but only the stress related to low GSH content, not that resulting from catalase inhibition, may be alleviated with Zn.
Title: Integrative assessment of biomarker responses in pale chub (Zacco platypus) exposed to copper and benzo[a]pyrene
Author(s): Kim, Woo-Keun; Lee, Sung-Kyu; Choi, Kyungho; et al.
Source: ECOTOXICOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY Volume: 92 Pages: 71-78 DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.02.010 Published: JUN 1 2013
Title: Effect of sarcosine on antioxidant parameters and metallothionein content in the PC-3 prostate cancer cell line
Author(s): Cernei, Natalia; Zitka, Ondrej; Skalickova, Sylvie; et al.
Source: ONCOLOGY REPORTS Volume: 29 Issue: 6 Pages: 2459-2466 DOI: 10.3892/or.2013.2389 Published: JUN 2013
Title: Holo-TFIID controls the magnitude of a transcription burst and fine-tuning of transcription
Author(s): Pennington, Katie L.; Marr, Sharon K.; Chirn, Gung-Wei; et al.
Source: PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Volume: 110 Issue: 19 Pages: 7678-7683 DOI:
Title: Metallothioneins negatively regulate IL-27-induced type 1 regulatory T-cell differentiation
Author(s): Wu, Chuan; Pot, Caroline; Apetoh, Lionel; et al.
Source: PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Volume: 110 Issue: 19 Pages: 7802-7807 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211776110 Published: MAY 7 2013
Abstract: IL-27-induced type 1 regulatory T (Tr1) cells suppress autoimmunity by producing IL-10. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 have been described as key transcription factors that promote IL-10 secretion from Tr1 cells induced by IL-27. However, the molecular pathways for negatively regulating Tr1 cell differentiation remain elusive. Here, we show that IL-27 induces metallothioneins (MTs) that in turn prevent Tr1 cell development. MT expression leads to the reduction of STAT1 and STAT3 phosphorylation under Tr1 differentiation condition, resulting in impaired IL-10 production. Accordingly, Tr1 cells derived from MT-deficient mice showed an increased ability to produce IL-10 and potently suppress experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis upon adoptive transfer. Moreover, activation of STAT1 and/or STAT3 can overcome the suppression of IL-10 by MTs, indicating a dynamic balance between STATs and MTs in regulating IL-10 during Tr1 cell differentiation.
Title: TISSUE-DEPENDENT METALLOTHIONEIN AND CYTOSOLIC METAL DISTRIBUTION IN A NATIVE CASPIAN SEA FISH, Acipenser persicus
Author(s): Shariati, Fatemeh; Pourkazemi, Mohammad; Shariati, Shayan; et al.
Source: FRESENIUS ENVIRONMENTAL BULLETIN Volume: 22 Issue: 5 Pages: 1408-1414 Published: 2013
Title: The involvement of metallothionein in rotenone-induced neurodegeneration in central and peripheral nervous systems
Author(s): Murakami, Shinki; Miyazaki, Ikuko; Torigoe, Nao; et al.
Conference: 86th Annual Meeting of the Japanese-Pharmacological-SocietyLocation: Fukuoka, JAPANDate: MAR 21-23, 2013
Sponsor(s): Japanese Pharmacol Soc
Source: JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGICAL SCIENCES Volume: 121 Supplement: 1 Pages: 220P-220P Published: 2013
Influenza
1. Title: Review: Influenza virus in pigsAuthor(s): Crisci, Elisa; Mussa, Tufaria; Fraile, Lorenzo; et al.
Source: MOLECULAR IMMUNOLOGY Volume: 55 Issue: 3-4 Pages: 200-211 DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.02.008 Published: OCT 2013
2. Title: Inferring patterns of influenza transmission in swine from multiple streams of surveillance data
Author(s): Strelioff, Christopher C.; Vijaykrishna, Dhanasekaran; Riley, Steven; et al.
Source: PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY B-BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Volume: 280 Issue: 1762 Article Number: 20130872 DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2013.0872 Published: JUL 7 2013
3. Title: Clinical characteristics and outcomes of influenza and other influenza-like illnesses in Mexico City
Author(s): Galindo-Fraga, Arturo; Ortiz-Hernandez, Ana A.; Ramirez-Venegas, Alejandra; et al.
Group Author(s): La Red ILI 002 Study Grp
Source: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Volume: 17 Issue: 7 Pages: E510-E517 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2013.01.006 Published: JUL 2013
4. Title: Molecular and phylogenetic analysis of influenza A H1N1 pandemic viruses in Cuba, May 2009 to August 2010
Author(s): Pinon Ramos, Alexander; Acosta Herrera, Belsy; Valdes Ramirez, Odalys; et al.
Source: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Volume: 17 Issue: 7 Pages: E565-E567 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2013.01.028 Published: JUL 2013
5. Title: Modeling the initial transmission dynamics of influenza A H1N1 in Guangdong Province, China
Author(s): Tan, Xuhui; Yuan, Lingling; Zhou, Jingjing; et al.
Source: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Volume: 17 Issue: 7 Pages: E479-E484 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2012.11.018 Published: JUL 2013
6. Title: Discovery of a series of novel compounds with moderate anti-avian H5N1 influenza virus activity in chick embryo
Author(s): Xie, Yuanchao; Huang, Bing; Yu, Kexiang; et al.
Source: MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY RESEARCH Volume: 22 Issue: 7 Pages: 3485-3496 DOI: 10.1007/s00044-012-0341-2 Published: JUL 2013
7. Title: A SOCIAL NETWORK INTERVENTION FOR REDUCING INFLUENZA-LIKE ILLNESS TRANSMISSION: THE EX-FLU CLUSTER RANDOMIZED TRIAL.
Author(s): Aiello, Allison E.; Volz, Erik; Simanek, Amanda M.; et al.
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S133-S133 Published: JUN 15 2013
8. Title: A NEW INDICATOR OF INFLUENZA INCIDENCE BASED ON VIRAL AND INFLUENZA-LIKE ILLNESS SURVEILLANCE DATA
Author(s): Foppa, Ivo; Reynolds, Sue
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S17-S17 Published: JUN 15 2013
9. Title: HETEROGENEITY IN SOCIAL CONTACT AMONG SCHOOL-AGE CHILDREN AND IMPLICATIONS FOR INFLUENZA TRANSMISSION
Author(s): Leecaster, Molly; Pettey, Warren; Toth, Damon; et al.
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S151-S151 Published: JUN 15 2013
10. Title: ESTIMATING THE INCIDENCE AND SEVERITY OF INFLUENZA IN THE UNITED STATES: A BAYESIAN PERSPECTIVE
Author(s): Reed, Carrie; Chaves, Sandra; Kirley, Pam Daily; et al.
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S110-S110 Published: JUN 15 2013
11. Title: MODELING THE POTENTIAL IMPACT OF AN INFLUENZA A/H3N2V VACCINE IN THE UNITED STATES
Author(s): Reed, Carrie; Borse, Rebekah; Gambhir, Manoj; et al.
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S111-S111 Published: JUN 15 2013
12. Title: A MATHEMATICAL MODEL FOR HERD IMMUNITY AGAINST INFLUENZA IN LONG-TERM CARE FACILITIES IN NEW MEXICO.
Author(s): Wendelboe, Aaron; Grafe, Carl; McCumber, Micah
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S133-S133 Published: JUN 15 2013
13. Title: PREDICTING INFLUENZA ADMISSIONS AMONG VETERANS FROM TELEPHONE TRIAGE
Author(s): Winston, Carla; Lucero-Obusan, Cynthia; Schirmer, Patricia; et al.
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S111-S111 Published: JUN 15 2013
14. Title: INFLUENZA VACCINATIONS FOR CHILDREN LIMITED BY UNMET HEALTHCARE NEED WITHIN THEIR FAMILIES
Author(s): Wisk, Lauren; Witt, Whitney
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S49-S49 Published: JUN 15 2013
15. Title: GUIDELINE APPROPRIATE RECEIPT OF THE INFLUENZA VACCINE AMONG PREGNANT WOMEN IN THE US.
Author(s): Wisk, Lauren; Witt, Whitney
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S162-S162 Published: JUN 15 2013
16. Title: CASE FATALITY RISK OF 2009 PANDEMIC INFLUENZA A(H1N1): A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS
Author(s): Wong, Jessica; Kelly, Heath; Ip, Dennis; et al.
Source: AMERICAN JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY Volume: 177 Supplement: 11 Pages: S111-S111 Published: JUN 15 2013
17. Title: Caffeic acid derivatives: A new type of influenza neuraminidase inhibitors
Author(s): Xie, Yuanchao; Huang, Bing; Yu, Kexiang; et al.
Source: BIOORGANIC & MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS Volume: 23 Issue: 12 Pages: 3556-3560 DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.04.033 Published: JUN 15 2013
18. Title: An insight into the PB1F2 protein and its multifunctional role in enhancing the pathogenicity of the influenza A viruses
Author(s): Chakrabarti, Alok K.; Pasricha, Gunisha
Source: VIROLOGY Volume: 440 Issue: 2 Pages: 97-104 DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.02.025 Published: JUN 5 2013
19. Title: Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae Internal quality control as a quality tool on a national level
Author(s): Karpanoja, Pauliina; Nissinen, Antti; Huovinen, Pentti; et al.
Group Author(s): Finnish Study Grp
Source: APMIS Volume: 121 Issue: 6 Pages: 561-568 DOI: 10.1111/apm.12021 Published: JUN 2013
20. Title: Immunogenicity and Safety of an Inactivated Trivalent Split Influenza Virus Vaccine in Young Children with Recurrent Wheezing
Author(s): Bae, E. Young; Choi, Ui Yoon; Kwon, Hyo Jin; et al.
Source: CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY Volume: 20 Issue: 6 Pages: 811-817 DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00008-13 Published: JUN 2013
21. Title: B Cell Response and Hemagglutinin Stalk-Reactive Antibody Production in Different Age Cohorts following 2009 H1N1 Influenza Virus Vaccination
Author(s): Sangster, Mark Y.; Baer, Jane; Santiago, Felix W.; et al.
Source: CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY Volume: 20 Issue: 6 Pages: 867-876 DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00735-12 Published: JUN 2013
22. Title: Case-Control Study of the Effectiveness of the 2010-2011 Seasonal Influenza Vaccine for Prevention of Laboratory-Confirmed Influenza Virus Infection in the Korean Adult Population
Author(s): Choi, Won Suk; Noh, Ji Yun; Seo, Yu Bin; et al.
Source: CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY Volume: 20 Issue: 6 Pages: 877-881 DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00009-13 Published: JUN 2013
23. Title: A magnetic bead-based bienzymatic electrochemical immunosensor for determination of H9N2 avian influenza virus
Author(s): Zhou, Chuan-Hua; Long, Yan-Min; Qi, Bao-Ping; et al.
Source: ELECTROCHEMISTRY COMMUNICATIONS Volume: 31 Pages: 129-132 DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2013.03.024 Published: JUN 2013
24. Title: Early application of high frequency oscillatory ventilation in 'H1N1 influenza' related ARDS is associated with better outcome: a retrospective study
Author(s): Jog, Sameer; Patel, Divyesh; Dravid, Tejal; et al.
Source: INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE Volume: 39 Issue: 6 Pages: 1146-1147 DOI: 10.1007/s00134-013-2878-z Published: JUN 2013
25. Title: Detection of pandemic influenza-A(H1N1)-2009 virus in urine
Author(s): Ho, Yeh-Li; Yoshino, Alessandra; Tonacio, Adriana Coracini; et al.
Source: INTENSIVE CARE MEDICINE Volume: 39 Issue: 6 Pages: 1168-1169 DOI: 10.1007/s00134-013-2921-0 Published: JUN 2013
26. Title: Transcriptome signature in young children with acute otitis media due to non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae
Author(s): Liu, Keyi; Chen, Linlin; Kaur, Ravinder; et al.
Source: INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOLOGY Volume: 25 Issue: 6 Pages: 353-361 DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxs154 Published: JUN 2013
27. Title: Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae Carbonic Anhydrase Is Important for Environmental and Intracellular Survival
Author(s): Langereis, Jeroen D.; Zomer, Aldert; Stunnenberg, Hendrik G.; et al.
Source: JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY Volume: 195 Issue: 12 Pages: 2737-2746 DOI: 10.1128/JB.01870-12 Published: JUN 2013
28. Title: Production of avian influenza virus vaccine using primary cell cultures generated from host organs
Author(s): Babar, Mustafeez Mujtaba; Riaz, Muhammad Suleman; Zaidi, Najam-us-Sahar Sadaf; et al.
Source: JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL MICROBIOLOGY & BIOTECHNOLOGY Volume: 40 Issue: 6 Pages: 625-632 DOI: 10.1007/s10295-013-1256-8 Published: JUN 2013
29. Title: Qualitative dynamics of lowly- and highly-pathogenic avian influenza strains
Author(s): Agusto, F. B.; Gumel, A. B.
Source: MATHEMATICAL BIOSCIENCES Volume: 243 Issue: 2 Pages: 147-162 DOI: 10.1016/j.mbs.2013.02.001 Published: JUN 2013
30. Title: Genetic Diversity of the ftsI Gene in beta-Lactamase-Nonproducing Ampicillin-Resistant and beta-Lactamase-Producing Amoxicillin-/Clavulanic Acid-Resistant Nasopharyngeal Haemophilus influenzae Strains Isolated from Children in South Korea
Author(s): Park, Chulmin; Kim, Kyung-Hyo; Shin, Na-Young; et al.
Source: MICROBIAL DRUG RESISTANCE Volume: 19 Issue: 3 Pages: 224-230 DOI: 10.1089/mdr.2012.0116 Published: JUN 2013
31. Title: Structural Insights on the Potential Significance of the Twin Asn-Residue Found at the Base of the Hemagglutinin 2 Stalk in All Influenza A H1N1 Strains: A Computational Study with Clinical Implications
Author(s): Cueno, Marni E.; Imai, Kenichi; Ochiai, Kuniyasu
Source: OMICS-A JOURNAL OF INTEGRATIVE BIOLOGY Volume: 17 Issue: 6 Pages: 297-301 DOI: 10.1089/omi.2012.0107 Published: JUN 2013
32. Title: Antibody Persistence for up to 5 Years After a Fourth Dose of Haemophilus influenzae Type b and Neisseria Meningitidis Serogroups C and Y-Tetanus Toxoid Conjugate Vaccine (HibMenCY-TT) Given at 12-15 Months of Age
Author(s): Marshall, Gary S.; Blatter, Mark; Marchant, Colin; et al.
Source: PEDIATRIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE JOURNAL Volume: 32 Issue: 6 Pages: 662-668 DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182840e35 Published: JUN 2013
33. Title: Effectiveness of Intranasal Live Attenuated Influenza Vaccine Against All-cause Acute Otitis Media in Children
Author(s): Heikkinen, Terho; Block, Stan L.; Toback, Seth L.; et al.
Source: PEDIATRIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE JOURNAL Volume: 32 Issue: 6 Pages: 669-674 DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182840fe7 Published: JUN 2013
34. Title: Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Caused by Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in a Previously Healthy Child
Author(s): Dimopoulou, Anastasia; Dimopoulou, Dimitra; Christianakis, Efstratios; et al.
Source: PEDIATRIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE JOURNAL Volume: 32 Issue: 6 Pages: 704-704 DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182869657 Published: JUN 2013
35. Title: Relationships Between Rhinitis Symptoms, Respiratory Viral Infections and Nasopharyngeal Colonization With Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus in Children Attending Daycare (vol 32, pg 227, 2013)
Author(s): Rodrigues, F.; Foster, D.; Nicoli, E.
Source: PEDIATRIC INFECTIOUS DISEASE JOURNAL Volume: 32 Issue: 6 Pages: 707-707 DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318298e62e Published: JUN 2013
36. Title: Immunogenicity of pandemic influenza A H1N1/2009 adjuvanted vaccine in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients
Author(s): Gavalda, J.; Cabral, E.; Perez-Romero, P.; et al.
Group Author(s): Spanish Network Res Infect Dis
Source: PEDIATRIC TRANSPLANTATION Volume: 17 Issue: 4 Pages: 403-406 DOI: 10.1111/petr.12084 Published: JUN 2013
37. Title: INFLUENZA A VIRUS H3N2 IS EFFICIENTLY INACTIVATED BY THE THERAFLEX UV-PLATELETS SYSTEM
Author(s): Gravemann, U.; Schmidt, J-P; Tolksdorf, F.; et al.
Source: VOX SANGUINIS Volume: 105 Special Issue: SI Supplement: 1 Pages: 134-134 Published: JUN 2013
38. Title: Double dose oseltamivir for severe influenza-does it help?
Author(s): Barr, Ian G.; Hurt, Aeron C.
Source: BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL Volume: 346 Article Number: f3449 DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f3449 Published: MAY 30 2013
39. Title: Effect of double dose oseltamivir on clinical and virological outcomes in children and adults admitted to hospital with severe influenza: double blind randomised controlled trial
Author(s): Sedyaningsih, Endang Rahayu; Malik, Moh Suhud; Setiawaty, Vivi; et al.
Group Author(s): South East Asia Infect Dis
Source: BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL Volume: 346 Article Number: f3039 DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f3039 Published: MAY 30 2013
40. Title: Exposure to avian influenza H7N9 in farms and wet markets
Author(s): Lee, Shui Shan; Wong, Ngai Sze; Leung, Chi Chiu
Source: LANCET Volume: 381 Issue: 9880 Pages: 1815-1815 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60949-6 Published: MAY 25 2013
41. Title: Reducing exposure to avian influenza H7N9
Author(s): Xu, Jianguo; Lu, Shan; Wang, Haiyin; et al.
Source: LANCET Volume: 381 Issue: 9880 Pages: 1815-1816 DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60950-2 Published: MAY 25 2013
42. Title: A Plant Extract of Ribes nigrum folium Possesses Anti-Influenza Virus Activity In Vitro and In Vivo by Preventing Virus Entry to Host Cells
Author(s): Ehrhardt, Christina; Dudek, Sabine Eva; Holzberg, Magdalena; et al.
Source: PLOS ONE Volume: 8 Issue: 5 Article Number: e63657 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063657 Published: MAY 23 2013
43. Title: Actin Mediates the Nanoscale Membrane Organization of the Clustered Membrane Protein Influenza Hemagglutinin
Author(s): Gudheti, Manasa V.; Curthoys, Nikki M.; Gould, Travis J.; et al.
Source: BIOPHYSICAL JOURNAL Volume: 104 Issue: 10 Pages: 2182-2192 DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.03.054 Published: MAY 21 2013
44. Title: Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia associated with influenza A/H1N1 pneumonia after lung transplantation
Author(s): Otto, Claudia; Huzly, Daniela; Kemna, Lars; et al.
Source: BMC PULMONARY MEDICINE Volume: 13 Article Number: 30 DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-13-30 Published: MAY 19 2013
45. Title: Genetic diversity of HA1 domain of heammaglutinin gene of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 in Tunisia
Author(s): El Moussi, Awatef; Kacem, Mohamed Ali Ben Hadj; Pozo, Francisco; et al.
Source: VIROLOGY JOURNAL Volume: 10 Article Number: 150 DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-150 Published: MAY 16 2013
46. Title: Synthetic Generation of Influenza Vaccine Viruses for Rapid Response to Pandemics
Author(s): Dormitzer, Philip R.; Suphaphiphat, Pirada; Gibson, Daniel G.; et al.
Source: SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE Volume: 5 Issue: 185 Published: MAY 15 2013
47. Title: Synthetic Generation of Influenza Vaccine Viruses for Rapid Response to Pandemics
Author(s): Dormitzer, Philip R.
Source: SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE Volume: 5 Issue: 185 Article Number: 185ra68 DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006368 Published: MAY 15 2013
48. Title: Risk factors associated with severe manifestations of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1) infection in China: a case-control study
Author(s): Ren, Yan-yan; Yin, Yu-yan; Li, Wen-qing; et al.
Source: VIROLOGY JOURNAL Volume: 10 Article Number: 149 DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-149 Published: MAY 15 2013
49. Title: Human monoclonal ScFv that bind to different functional domains of M2 and inhibit H5N1 influenza virus replication
Author(s): Pissawong, Tippawan; Maneewatch, Santi; Thueng-in, Kanyarat; et al.
Source: VIROLOGY JOURNAL Volume: 10 Article Number: 148 DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-148 Published: MAY 14 2013
50. Title: Association of RIG-I with innate immunity of ducks to influenza (vol 107,pg 5913,2010)
Author(s): Barber, Megan R. W.; Aldridge, Jerry R., Jr.; Webster, Robert G.; et al.
Source: PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA Volume: 110 Issue: 19 Pages: 7958-7958 DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1306250110 Published: MAY 7 2013
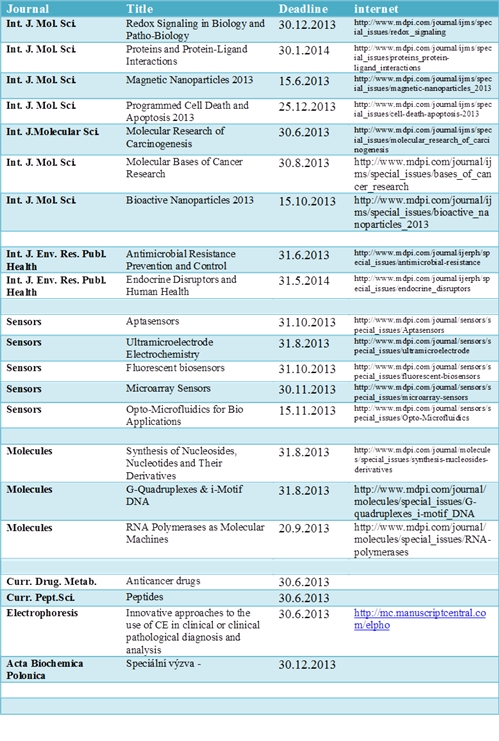
Aktuální výzvy pro speciální čísla časopisů/Current calls for a special issues
ODKAZY | LINKS




NOVÉ PUBLIKACE
Nanoparticles-based Carriers for Gene Therapy and Drug Delivery
Chemical Vapour Depositions for Carbon Nanotubes Synthesis
Quantum Dots:Biological and biomedecical applications
Archiv
23_201322_2013
21_2013
20_2013
19_2013
18_2013
17_2013
16_2013
15_2013
14_2013
13_2013
12_2013
11_2013
10_2013
09_2013
08_2013

 | Zemědělská 1/1665 613 00 Brno Budova D | Tel.: +420 545 133 350 Fax.: +420 545 212 044 |  |
 |



















