
Bacteriophage λ as a doxorubicin nanocarrier
Simona Dostalova, Marketa Vaculovicova, Rene Kizek
In this study, we discussed the use of bacteriophage λ as a nanocarrier of anthracycline drug doxorubicin. This drug is used in treatment of cancer, which is the cause of death of every fourth patient in developed countries. Doxorubicin has many severe side effects for patients’ healthy cells, which lowers their well-being. These can be eliminated by encapsulation of doxorubicin into suitable nanocarrier, such as bacteriophage λ capsid. In this work, infusion method was used for this encapsulation and proven by absorbance and fluorescence measurement of whole bacteriophage. It was concluded, that bacteriophage both intercalates into DNA and binds to capsid proteins of bacteriophage λ.
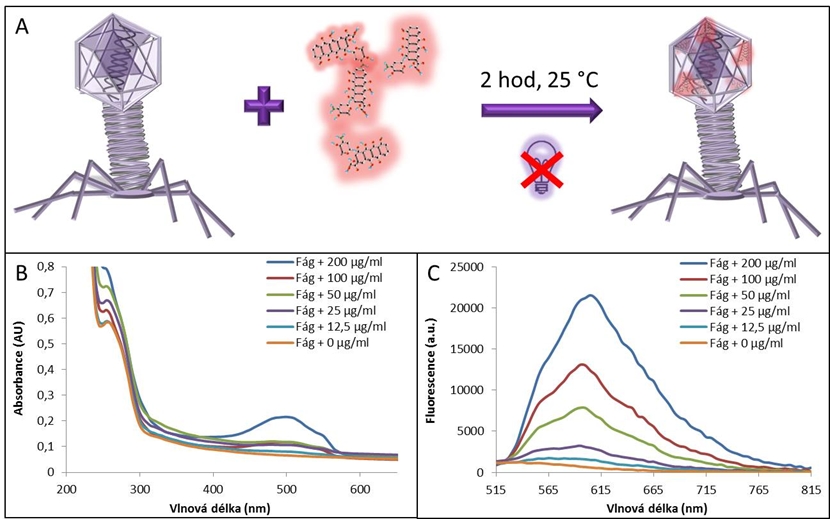
Fig. 1: Encapsulation of various concentrations of doxorubicin into bacteriophage λ. A) Schematic encapsulation. B) infrared absorption spectrum of the bacteriophage with encapsulated doxorubicin, wavelength 230-650 nm. C) Fluorescence spectrum Bacteriophage with encapsulated doxorubicin, excitation wavelength 480 nm, emission wavelength 515-815 nm.
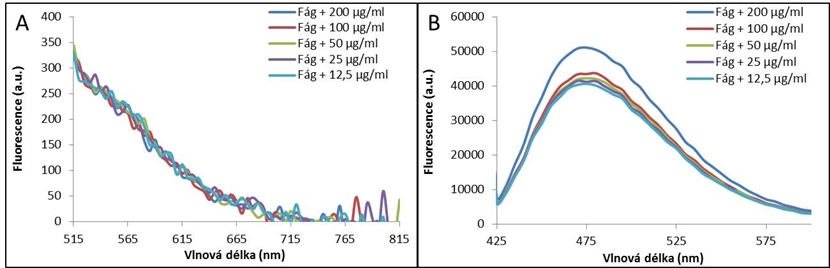
Fig. 2: Visualization of doxorubicin in bacteriophage λ DNA. A) Fluorescence spectrum of the isolated DNA of bacteriophage λ with encapsulated doxorubicin, excitation wavelength 480 nm, emission wavelength 515-815. B) Fluorescent spectrum fluorescamine derivatization reagent bound to the primary amino groups of doxorubicin after 5 minute incubation, excitation wavelength 390 nm, emission wavelength 425-600 nm.
1. Sumer, B.; Gao, J.M. Theranostic nanomedicine for cancer. Nanomedicine. 2008, 3, 137-140.
2. Negreira, N.; Mastroianni, N.; de Alda, M.L.; Barcelo, D. Multianalyte determination of 24 cytostatics and metabolites by liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry and study of their stability and optimum storage conditions in aqueous solution. Talanta. 2013, 116, 290-299.
3. Kizek, R.; Adam, V.; Hrabeta, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Smutny, S.; Burda, J.V.; Frei, E.; Stiborova, M. Anthracyclines and ellipticines as DNA-damaging anticancer drugs: Recent advances. Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2012, 133, 26-39.
4. Minotti, G.; Menna, P.; Salvatorelli, E.; Cairo, G.; Gianni, L. Anthracyclines: Molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacological Reviews. 2004, 56, 185-229.
5. Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Poljakova, J.; Hrabeta, J.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R.; Frei, E. The Synergistic Effects of DNA-Targeted Chemotherapeutics and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors As Therapeutic Strategies for Cancer Treatment. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2012, 19, 4218-4238.
6. Bean, J.F.; Qiu, Y.-Y.; Yu, S.; Clark, S.; Chu, F.; Madonna, M.B. Glycolysis inhibition and its effect in doxorubicin resistance in neuroblastoma. Journal of pediatric surgery. 2014, 49, 981-984.
7. Szwed, M.; Matusiak, A.; Laroche-Clary, A.; Robert, J.; Marszalek, I.; Jozwiak, Z. Transferrin as a drug carrier: Cytotoxicity, cellular uptake and transport kinetics of doxorubicin transferrin conjugate in the human leukemia cells. Toxicology in Vitro. 2014, 28, 187-197.
8. Burley, K.; Allford, S. Managing the risk of cardiotoxicity: an audit of lymphoma patients receiving doxorubicin-based chemotherapy at Musgrove Park Hospital, Taunton. British Journal of Haematology. 2014, 165, 70-70.
9. Kitamura, H.; Tsukamoto, T.; Shibata, T.; Masumori, N.; Fujimoto, H.; Hirao, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Tomita, Y.; Tobisu, K.; Niwakawa, M.; Naito, S.; Eto, M.; Kakehi, Y.; Urologic Oncology Study Group of the Japan Clinical Oncology, G. Randomised phase III study of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with methotrexate, doxorubicin, vinblastine and cisplatin followed by radical cystectomy compared with radical cystectomy alone for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG0209. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology / ESMO. 2014, 25, 1192-1198.
10. Condello, M.; Cosentino, D.; Corinti, S.; Di Felice, G.; Multari, G.; Gallo, F.R.; Arancia, G.; Meschini, S. Voacamine Modulates the Sensitivity to Doxorubicin of Resistant Osteosarcoma and Melanoma Cells and Does Not Induce Toxicity in Normal Fibroblasts. Journal of Natural Products. 2014, 77, 855-862.
11. Manocha, B.; Margaritis, A. Controlled release of doxorubicin from doxorubicin/gamma-polyglutamic acid ionic complex. Journal of Nanomaterials. 2010.
12. Zhang, S.; Liu, X.B.; Bawa-Khalfe, T.; Lu, L.S.; Lyu, Y.L.; Liu, L.F.; Yeh, E.T.H. Identification of the molecular basis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nature Medicine. 2012, 18, 1639-+.
13. Park, K. Facing the truth about nanotechnology in drug delivery. ACS Nano. 2013, 7, 7442-7447.
14. Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Drug delivery systems: Entering the mainstream. Science. 2004, 303, 1818-1822.
15. Duncan, R.; Sat, Y.N. Tumour targeting by enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Annals of Oncology. 1998, 9, 39-39.
16. Maeda, H. Macromolecular therapeutics in cancer treatment: The EPR effect and beyond. Journal of Controlled Release. 2012, 164, 138-144.
17. Svenson, S. Theranostics: Are we there yet? Molecular Pharmaceutics. 2013, 10, 848-856.
18. Peer, D.; Karp, J.M.; Hong, S.; FaroKhzad, O.C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nature Nanotechnology. 2007, 2, 751-760.
19. Snustad, D.P.; Simmons, M.J. Genetika, Nakladatelstvi Masarykovy univerzity, Brno, 2009.
20. Yildiz, I.; Lee, K.L.; Chen, K.; Shukla, S.; Steinmetz, N.F. Infusion of imaging and therapeutic molecules into the plant virus-based carrier cowpea mosaic virus: Cargo-loading and delivery. Journal of Controlled Release. 2013, 172, 568-578.
21. Huska, D.; Adam, V.; Babula, P.; Hrabeta, J.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Trnkova, L.; Kizek, R. Square-wave voltammetry as a tool for investigation of doxorubicin interactions with DNA isolated from neuroblastoma cells. Electroanalysis. 2009, 21, 487-494.
22. Changenet-Barret, P.; Gustavsson, T.; Markovitsi, D.; Manet, I.; Monti, S. Unravelling molecular mechanisms in the fluorescence spectra of doxorubicin in aqueous solution by femtosecond fluorescence spectroscopy. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2013, 15, 2937-2944.
J.Met.Nano:
volume-1, issue-3
- Personal and professional representation of the nanolabsys project
- Administration and information system of the project
- Microwave preparation of carbon quantum dots with different surface modification
- Cell lines as a model system for quantum dots applications
- Application of quantum dots into chicken embryos
- The influence of zinc to living organisms
- The influence of cadmium to living organisms
- The influence of lead to living organisms
- The influence of mercury to living organisms
- Monitoring of metallothionein levels in biological organism exposed to the metal elements and compounds
- The ratio of GSH/GSSG in biological organisms
- Amino Acids and their interactions with heavy metals
- Antioxidat enzymes – biochemical markers of oxidative stress
- Study of the interaction of quantum dots with tumor cells by fluorescence microscopy
- Flow-cytometric analysis of programmed cell death
- Bacteriophage λ as a doxorubicin nanocarrier
 PDF
PDF